Understanding bullish vs bearish trends helps investors make smarter decisions by recognizing shifts in market sentiment and direction early.
What Are Bullish and Bearish Trends?
Market trends show us how prices change over a specific period. We can categorize these trends into two primary types.
1. Bullish Trend (Uptrend)
When the price of certain assets consistently rises, we refer to the market as bullish. Key characteristics include.
- Price charts have been making higher highs and higher lows.
- The trading volumes go up during upward movements or trends.
- The news is positive, including earnings beats, victories with regulators, and challenges to the macro framework.
For instance, Bitcoin rose from $10,000 to nearly $70,000 in 2021, a classic bull run due to institutional adoption and retail enthusiasm.
2. Bearish Trend (Downtrend)
A bearish trend refers to negative investor sentiment wherein asset prices are falling and likely to continue falling in the near future. Characteristics include.
- There have been lower highs and lower lows on price charts.
- The trading volumes decline during downward moves.
- Some negative catalysts are regulatory crackdowns, weak earnings, and a global slowdown.
Many tokens fell by more than 70% during the 2022 crash of digital currencies. This period is a protracted bear market due to macroeconomic pressures and liquidity challenges.
How to Identify Bullish and Bearish Trends
If you spot upcoming trends early, it enables you to seize opportunities or protect your portfolio. Learn How To Identify These Markets’ Trends Through Technical Analysis, Fundamental Factors and Sentiment Indicators.
1. Technical Analysis Tools
Technical indicators give objective data confirming trends.
a. Moving Averages (MA).
- An upward trend happens when a short-term moving average, like the 50-day MA, crosses above a longer-term moving average, like the 200-day MA. This phenomenon is called a golden cross.
- A death cross will form when certain things happen in a downturn.
b. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
- An RSI over seventy means it is overbought and may signal a possible top.
- When the RSI score falls below 30, it suggests that a reversal of the bearish trend is likely in the offing.
c. Trendlines.
- In an uptrend, draw trendlines from higher lows, and in a downtrend, draw trendlines from lower highs to show the direction.
2. Candlestick Patterns
- Candlestick charts illustrate short-term price movements and help identify reversal patterns within a market.
- Bullish patterns include the hammer, bullish engulfing, and morning star. These patterns show that buying pressure is coming in.
Bearish Patterns: A reversal pattern shows that buyers are losing momentum.
3. Volume Analysis
- Volume confirms the strength of a trend.
- Rising volume during an uptrend validates bullish momentum.
- Declining volume in a downtrend signifies weakening selling.
4. Fundamental Factors
- Project-specific and economic fundamentals are critical.
- There are several important factors, including positive earnings, partnerships, regulatory clarity, and adoption metrics.
Negative factors include disappointing earnings, hacks, restrictions, and less user activity.
5. Sentiment Indicators
RATINGS are calculated using quantitative parameters, as well as psychological market gauges such as social…
- When investors become too greedy, it’s a sign that the market is too high.
- When extreme fear occurs, oftentimes reversals happen.
- Understanding Market Psychology Behind Trends.
In FinTech, it is not enough to rely on a statistical analysis to make investment decisions.
1. Bull Markets: Optimism Reigns
- Investor confidence causes bullish trends to occur.
- There has been an increase in risk appetite.
- FOMO (fear of missing out) is driving buying sprees.
Increased speculation in sectors such as crypto is on the rise.
2. Fear takes over during bear markets
- In bad times, people experience fear, which results in a down market.
- Investors are panic-selling as they rush to exit positions.
- There has been a reduction of liquidity and tight credit conditions.
- Optimistic stories ignore positive developments of the past few years.
- Strategies for Navigating Bullish and Bearish Trends.
Here’s how to position yourself when you know which way the wind is blowing
1. Trade in a Bull Market
- When prices fall, that is a good time to buy.
- Always place a stop loss a little below the critical support levels to protect profits.
- Trade on Breakouts: Enter after price breaks resistance at high volume.
2. Surviving a Bear Market
- Use options, futures and stablecoins to hedge your portfolio.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA): Gradually buying dips to lower purchase price.
Make every effort to stay true to the fundamentals and invest in projects with solid use cases that will survive down cycles.
3. Swing Trading Across Trends
Traders swing in the hope of making a profit on short- to medium-term price fluctuations, regardless of the trend.
- In bullish trends, target quick profits on pullbacks.
- A bear market allows you to short-sell or profit from volatility.
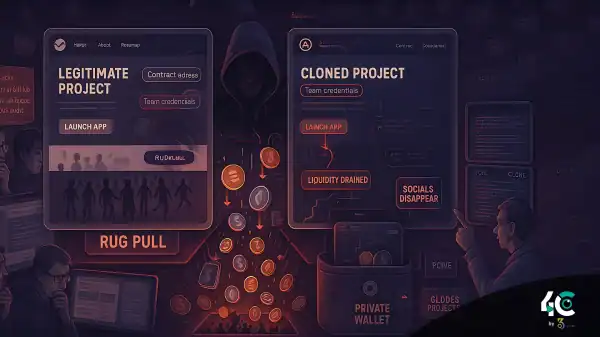
- There are common mistakes to avoid.
Misinterpreting trends can lead to costly errors. Here are pitfalls to watch out for
1. Overreacting to Short-Term Noise
Temporary corrections are not full reversals. Use multiple indicators to confirm trends.
2. Ignoring Risk Management
Not choosing stop losses or not allocating your capital properly can increase your losses.
3. Chasing Momentum Blindly
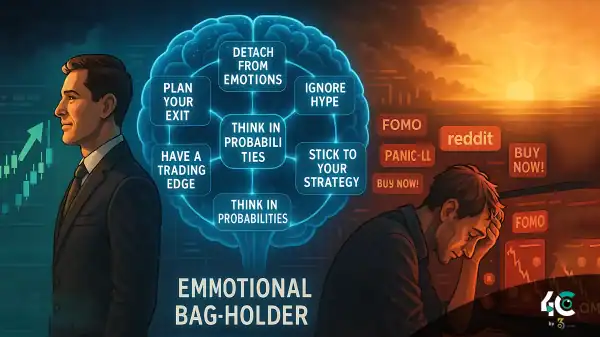
There are profits to be made during a bull market, but if you enter late or exit early, you will lose. Stick to your strategy.
Final Thoughts: Mastering Market Trends
Being aware of bullish and bearish trends will allow you to make your decisions and adapt. Combining fundamental analysis with human sentiment analysis and technical forecast analysis helps identify trends early.
Remember, no trend lasts forever—markets are cyclical. Whether the market is experiencing a bull rally or a bear slump, the key to making money in stocks is discipline and patience.
Conclusion
The bullish trend has rising price levels, higher lows, and an optimistic sentiment. A bearish trend has falling prices, lower highs, and a negative attitude. In a bull market, buy the dip; in a bear market, hedge; and avoid overreacting to the noise, which is something that most other investors tend to do. Bull or bear, with the right mindset and tools at your disposal, you can thrive.